
Two popular technologies that enhance security and privacy are SSH (Secure Shell) and VPN (Virtual Private Network). Both technologies are critical in safeguarding data as it traverses the internet, but they serve different purposes and operate in distinct ways.
- What is SSH?
- How SSH works
- Key functions of SSH
- The role of public-key cryptography in SSH
- What is a VPN?
- How VPNs enhance online security
- Changing your IP location
- VPNs in corporate and private environments
- Key differences between SSH and VPN
- Security of SSH and VPN
- SSH: Pros and Cons
- VPN: Pros and Cons
- Conclusion
What is SSH?
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a protocol designed to provide secure network communications on an unsecured network by using a method known as public-key cryptography. This protocol allows the seamless and secure operation of network devices through a client-server setup, where an SSH-supporting application on one device connects to an SSH server on another.
How SSH works
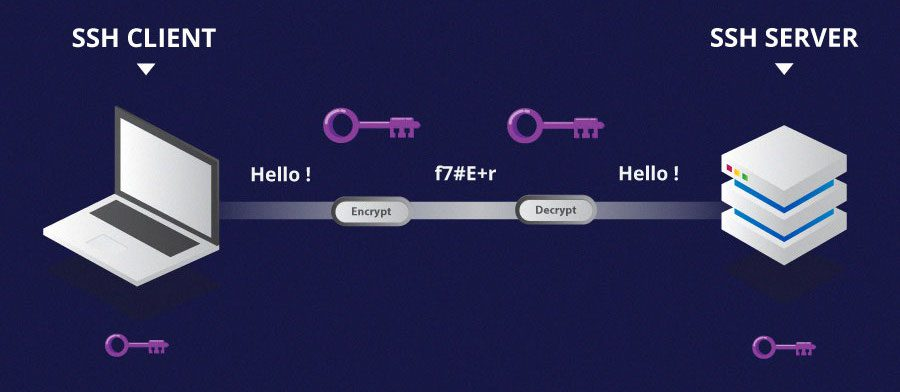
At its core, SSH operates on the client-server principle. A user or client uses SSH client software to connect to a host or an SSH server. The communication between the client and the server is encrypted, ensuring that all data transmitted over the network remains confidential and tamper-proof.
Key functions of SSH
SSH is versatile, primarily known for securing network services like command lines, system logins, and remote commands. It enables users to safely access and manage computers over an insecure network, such as the internet, from anywhere in the world. For example, a system administrator can use SSH to remotely manage servers, update configurations, or troubleshoot network issues without the need for physical access to each device.
Beyond command execution, SSH is also extensively used for secure file transfers. Protocols like SCP (Secure Copy Protocol) and SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) leverage SSH to protect the integrity and confidentiality of files as they move across an unsecured network.
The role of public-key cryptography in SSH
One of the pillars of SSH's security is its use of public-key cryptography for authentication. In this system, two keys are used: a public key and a private key. The public key can be shared with anyone, while the private key must be kept secure by the user. During the SSH authentication process, the server verifies the identity of the user by creating a challenge that can only be answered using the correct private key. If the response is correct, the server grants access, ensuring that only users with the correct private keys can access the system or data.
This method of authentication not only enhances security but also simplifies the login process as it can eliminate the need for passwords, which can be vulnerable to theft or brute force attacks.
What is a VPN?
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a technology designed to secure your internet connection by encrypting all traffic that passes through it and routing this encrypted traffic through a remote server before it reaches the internet. This process not only secures your data but also masks your geographical location by changing your IP address.
How VPNs enhance online security
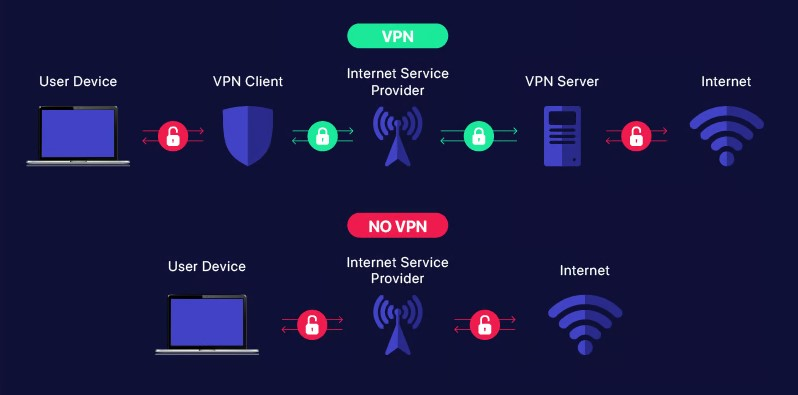
The core function of a VPN is to create a secure tunnel for your internet traffic. When you activate a VPN, it encrypts your data at the point of origin, which prevents anyone on the same network from eavesdropping on your activities. This encryption remains intact until your data reaches the VPN server, where it is decrypted and sent to its final destination on the open internet.
This encryption is vital not just for security but also for privacy. It ensures that sensitive information such as passwords, financial details, and personal emails are protected from interceptors like hackers or even internet service providers who might want to monitor or log your online behavior.
Changing your IP location
One of the most distinctive features of a VPN is its ability to change your IP location. By routing your connection through a server in a different geographic location, VPNs can make it appear as if you are accessing the internet from there. This capability is particularly useful for bypassing geo-restrictions on content, which can be beneficial for accessing regional news, streaming services, or even avoiding censorship in restrictive countries.
VPNs in corporate and private environments
VPNs are widely used in both corporate and private settings. In a corporate context, VPNs are crucial for providing employees secure access to internal networks and resources while they are outside of the corporate firewall, such as when working remotely or traveling. For private users, VPNs offer an essential layer of security, especially when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks, which are often insecure and expose users to potential threats.
Key differences between SSH and VPN

The fundamental difference between SSH and VPN lies in their scope and application:
- SSH encrypts the connection between two computers, typically for specific tasks like secure file transfers (SFTP) or remote system management. It is not designed to handle all traffic from a device but is highly effective for the secure administration of servers and other remote systems.
- VPN encrypts all traffic from a device to the internet. This includes all applications, services, and online activities, making it a versatile solution for general privacy and security across all internet usage. VPNs are often used to protect all data transmissions, not just those involving sensitive information.
Security of SSH and VPN
SSH is renowned for its security capabilities in specific scenarios, particularly secure remote logins to servers and other network services over an insecure network. It provides robust security for command-line-based communications and the secure transfer of files. SSH encrypts these communications effectively, protecting the data from potential eavesdropping and interception. This makes SSH especially valuable for system administrators and IT professionals who manage servers and need a secure way to handle sensitive operations remotely.
Conversely, VPNs are designed to secure all internet traffic from a user's device, not just individual network services. VPNs encrypt entire data packets, including the headers, which contain critical routing and IP information. This level of encryption enhances user privacy across all online activities, shielding data from internet service providers, potential government surveillance, and risks associated with using public Wi-Fi networks.
SSH: Pros and Cons

Pros of SSH
- Ease of setup (for IT Professionals). SSH is relatively straightforward to set up on a server level for users who have IT knowledge. This accessibility makes it a popular choice among system administrators and developers.
- Robust encryption. One of the strongest points of SSH is its ability to encrypt data transmission. This encryption protects against several types of cyber threats, including DNS spoofing, IP address hijacking, IP source routing, and general data theft. By securing data in transit, SSH ensures that sensitive information remains confidential and secure.
- Remote server management. SSH is particularly favored by webmasters for remote server control. It allows for easy management of web server accounts, making it a valuable tool for hosting control.
- Efficient permission and password management. SSH also facilitates easier management of permissions and password sharing, streamlining the administrative overhead and enhancing security practices within an organization.
Cons of SSH
- Setup complexity for novices. While SSH can be straightforward for IT professionals, it might present a challenge for users without technical expertise. The initial configuration and ongoing management require a certain level of IT knowledge, which can be a barrier for less experienced users.
- Limited to application-level encryption. Unlike VPNs, which encrypt all traffic from a device, SSH encrypts only the data pertaining to specific applications. This means that for each application that needs secure communication, separate configuration is necessary. This can be cumbersome if multiple applications require secure connections, and it leaves other parts of a user's internet traffic unencrypted.
VPN: Pros and Cons
Pros of a VPN
- Comprehensive encryption. A significant advantage of VPNs is their ability to encrypt all outgoing and incoming traffic from your device. This encryption can also be extended to your entire network if the VPN is set up at the router level, ensuring that all connected devices benefit from enhanced security.
- Global server access. Premium VPN services provide access to a vast network of servers worldwide. This feature allows users to change their virtual location by connecting to a server in a different country, which can be particularly useful for bypassing geo-restrictions and accessing content not available in one's own region.
- User-friendly. VPNs are generally user-friendly, even for those with little to no technical expertise. Many premium VPNs come with features like a "Quick Connect" button, which automatically selects the best server based on your location and server load, making the process straightforward and hassle-free.
- Reliable customer support. Legitimate premium VPN providers offer transparency about their operations and typically provide robust customer service. This support can be invaluable, especially if you encounter issues or have questions about using the service.
Cons of a VPN
- Complexity in server-level setup. While personal VPN applications are usually straightforward to use, setting up a VPN at the server level can be more complex and may require technical knowledge. This might pose a challenge for users or organizations without IT support.
- Risks of free VPN services. It's important to exercise caution when considering free VPN services. Many free VPNs may not provide reliable security; they might collect and sell your data to third parties, display intrusive ads, or offer inadequate encryption. In contrast, paid VPN services generally offer better security and do not involve such privacy risks.
Conclusion
SSH and VPN are both essential tools in the arsenal of internet security measures, each serving specific needs. SSH is optimal for secure, targeted access and tasks involving specific machines or servers. VPNs offer comprehensive security that covers all internet activity, suitable for users seeking privacy and extensive access across potentially restricted networks.
Choosing between SSH and VPN depends on one's specific needs—whether it's securing particular data channels or safeguarding all online activities. Both technologies continue to evolve, playing pivotal roles in the ongoing challenge of maintaining security and privacy in the digital realm.




Comments 0