
In 2024, the dark web remains a realm of the internet that offers both anonymity and privacy but also poses significant risks. Dark web marketplaces, which operate away from the prying eyes of conventional search engines and government oversight, can be hotspots for illegal activities, including the trade of illicit goods and services. However, with the right knowledge and precautions, individuals can navigate these murky waters safely.
- What is the Dark Web?
- What is a Dark Web market?
- Scams on Dark Web marketplaces
- Examples of historical Dark Web marketplaces
- Essential safety tips for navigating Dark Web marketplaces
- The future of Dark Web marketplaces
- Conclusion
What is the Dark Web?
The Dark Web refers to a segment of the internet that is not indexed by traditional search engines and remains hidden from the average user. It is accessible only through specialized software such as Tor (The Onion Router), which anonymizes user identities and activities to protect their privacy and security. This hidden part of the internet is often associated with a haven for illegal activities, including the sale of illicit drugs, firearms, and stolen data. However, it's important to recognize that the Dark Web also serves as a critical resource for whistleblowers, activists, and others who need to operate anonymously to protect themselves from retaliation or censorship in oppressive regimes.
What is a Dark Web market?
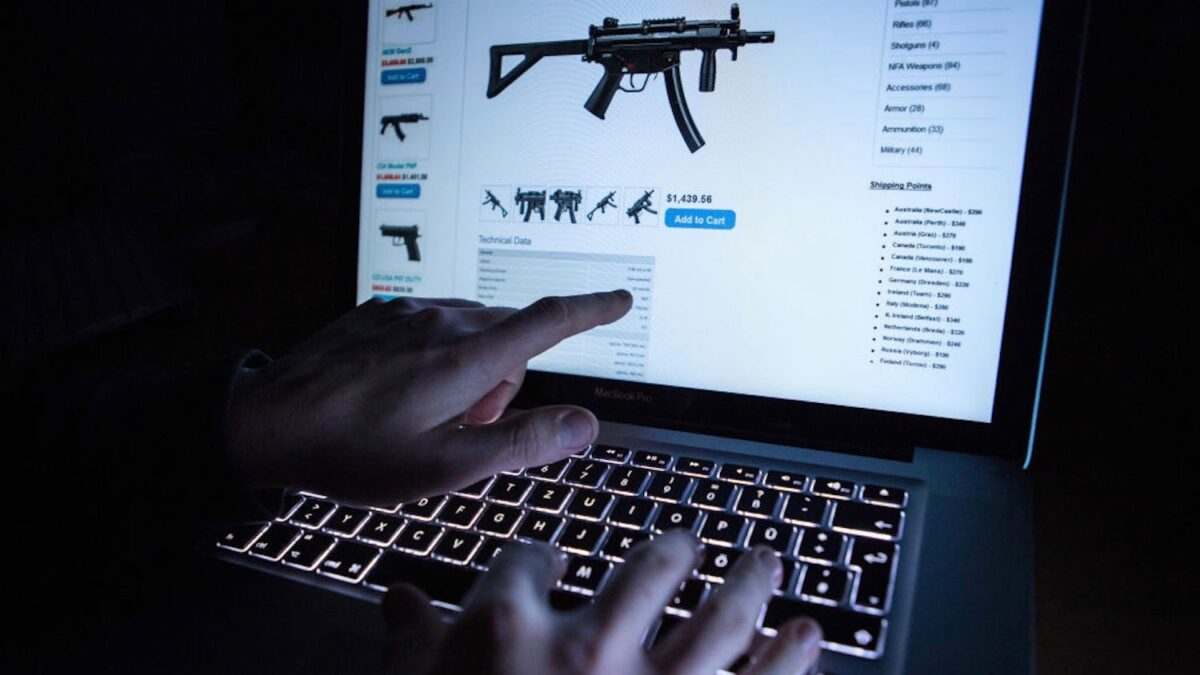

A Dark Web market is a type of online marketplace accessible only through networks like Tor that use anonymity tools to hide the identities of users and operators. These markets function similarly to legitimate e-commerce websites, but they are hidden from the typical web, making them part of the internet's dark side.
Darknet markets are notorious for their wide array of offerings, many of which are illegal or regulated substances and items. Here’s a closer look at what is commonly sold on these markets:
- Drugs: The most common listings on darknet markets are for various types of drugs. This includes everything from cannabis to psychedelics and prescription medications.
- Counterfeit goods: These markets also serve as a hub for counterfeit products, including fake identification documents like passports and driver’s licenses, counterfeit currency, and pirated software or media.
- Cybercrime tools: Items such as malware, hacking tools, or services like distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks can be bought. This category also includes services related to hacking social media accounts, corporate espionage, and more.
- Weapons: While less common than other goods, some darknet markets offer firearms and ammunition. These listings are highly illegal and carry significant risks.
- Miscellaneous illegal services: This can include anything from the hiring of hitmen (though often these are scams) to the acquisition of stolen credit card details or other personal information.
Despite the variety of items sold, it’s crucial to remember that engaging with darknet markets involves significant legal and personal risks. Many goods and services offered on these platforms are illegal and can lead to serious consequences, including imprisonment. As such, while it’s important to be aware of what happens on darknet markets, participating in them is not advisable.
Scams on Dark Web marketplaces
Dark Web marketplaces, although offering a high degree of anonymity and operating beyond the reach of conventional regulatory frameworks, are fraught with scams and fraudulent activities.
- Exit scams. Exit scams are particularly prevalent in the dark web ecosystem. Marketplace operators establish credibility by conducting seemingly legitimate transactions. Over time, as trust builds, they accumulate a significant amount of money in escrow—only to vanish, leaving buyers and sellers without their funds.
- Phishing attacks. Phishing is as rampant on the dark web as it is on the rest of the internet. Users often encounter fake websites that mimic legitimate marketplaces. These sites collect personal information and login credentials, which can be used for identity theft and financial fraud.
- Malware sales. The dark web serves as a marketplace for buying and selling malware. Unwary users looking for software may instead download malware, which is then used to infiltrate their devices to steal data or commit other forms of cyber fraud.
- Ponzi schemes. These fraudulent investment scams promise low-risk returns that seem unusually high. Operators pay returns to early investors using the capital of newer investors. However, such schemes are doomed to collapse once the flow of new investors dwindles, leading to substantial financial losses for most involved.
- Money laundering services. The anonymity of the dark web also makes it an attractive platform for money laundering. Individuals and groups use cryptocurrencies and complex transfer systems available on the dark web to obscure the origins of illicitly obtained funds.
Examples of historical Dark Web marketplaces
Silk Road
Launched in 2011, Silk Road is one of the most infamous dark web marketplaces. It was predominantly used for selling illegal drugs. The site was a pioneer in using Tor and Bitcoin to maintain anonymity. Silk Road was shut down by the FBI in 2013, and its founder was arrested.
AlphaBay
AlphaBay was another major player in the dark web market scene, which became operational in 2014 and was shut down by law enforcement in 2017. It was much larger than Silk Road and dealt in a wide range of illegal goods and services.
Hansa market
Hansa was known for its security-conscious design to protect the anonymity and security of its transactions. However, it was covertly taken over by law enforcement in 2017 at the same time AlphaBay was shut down. Authorities then used the site to gather data on vendors and customers, leading to numerous arrests.
Hydra market
Hydra Market, one of the largest dark web marketplaces catering primarily to Russian-speaking users, was shut down in 2022. German authorities, in cooperation with international law enforcement agencies including the FBI, seized Hydra's servers and eliminated over 17 million customer accounts and 19,000 seller accounts.
These examples serve to understand the general nature of dark web marketplaces and the potential consequences of participating in such sites. Due to the dynamic nature of the dark web, new marketplaces frequently emerge as others close, but they all face the inherent risks of operating in such part of the internet.
Essential safety tips for navigating Dark Web marketplaces

Use proper anonymization tools
Before accessing any dark web site, ensure that you are using Tor or a similar service to mask your IP address. Consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) in conjunction with Tor to add an extra layer of security. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, further preventing outsiders from tracing your activities back to you.
Employ robust cybersecurity measures
Maintain strong cybersecurity practices. This includes using complex passwords, employing two-factor authentication (2FA) where possible, and regularly updating your software to protect against vulnerabilities. Also, consider using a dedicated device or a secure operating system like TAILS (The Amnesic Incognito Live System) for dark web activities.
Verify identities and reviews
Just as with eBay or Amazon, check the credibility of sellers on dark web marketplaces. Read reviews and check ratings, but remain skeptical as these can be manipulated. Look for vendors who have long-standing reputations and those who are verified by the marketplace administrators.
Be cautious with payment methods
Cryptocurrency transactions are standard on the dark web, offering both parties anonymity. Use a cryptocurrency that promotes additional privacy (like Monero), and consider using a cryptocurrency tumbler or mixer to further obscure the transaction path.
Avoid oversharing personal information
Never share personal information, such as your real name, address, or phone number. Use encrypted messaging services to communicate with sellers, and always opt for service providers that prioritize user privacy.
Be aware of legal consequences
Understand the laws regarding online purchases and sales in your jurisdiction. Remember that buying or selling illegal items is prosecutable under law, regardless of the anonymity provided by the dark web.
Disable JavaScript and Flash
While Tor Browser disables JavaScript by default on all .onion sites, it's wise to ensure it's turned off when accessing any dark web marketplace. JavaScript can be exploited to reveal your real IP address or execute malicious code on your computer. Flash should be disabled or, better yet, completely uninstalled. Flash is known for being highly vulnerable to security exploits, and like JavaScript, can potentially expose your real IP address.
Do not download files
Downloading files from dark web marketplaces can be risky. Malicious files can compromise your device with malware or ransomware. If downloading is absolutely necessary, ensure to open the files while offline or in a secure environment, such as a virtual machine, which isolates them from the rest of your system.
Be skeptical of links and attachments
As with phishing attacks on the surface web, be extremely cautious about clicking on links or opening attachments on the dark web. These can often be traps designed to compromise your security.
The future of Dark Web marketplaces

Enhanced anonymity and security measures
In response to increasing crackdowns by law enforcement, dark web marketplaces are likely to implement even more robust security measures. Technologies like blockchain and advancements in encryption methods are set to play a significant role. Operators and users will seek new ways to ensure anonymity, possibly moving towards decentralized platforms that lack a single point of failure and are harder to shut down.
Increased use of cryptocurrencies
While Bitcoin remains popular, the future will see a broader adoption of various other cryptocurrencies, especially those that offer greater privacy, such as Monero and Zcash. These currencies help obscure transaction details, providing an additional layer of security to users keen on maintaining their anonymity.
Shift towards decentralization
The centralization of marketplace platforms has often led to massive takedowns. In response, the future may favor decentralized market models. Technologies such as decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) could allow marketplaces to operate without a centralized authority, potentially reducing the risk of mass takedowns.
Integration of artificial intelligence
AI and machine learning could be increasingly used to navigate complex market dynamics, optimize security, and enhance the user experience. However, these technologies might also be employed in policing these platforms, as authorities use advanced tools to analyze data and identify illegal activities.
Increased market fragmentation
Future marketplaces may see increased fragmentation. Instead of a few large players, many smaller, niche markets could emerge, each catering to specific goods or services. This fragmentation could make it harder for law enforcement to monitor and control illegal activities.
Conclusion
Navigating dark web marketplaces in 2024 requires caution, preparation, and a strong awareness of both the technological and legal risks involved. By employing robust security measures and practicing vigilant online behavior, users can significantly mitigate the risks associated with these secretive digital marketplaces.




Comments 0