
Introduction
Encryption, the process of encoding information to protect its confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity, has evolved significantly over time. As cyber threats grow in complexity, the development and application of diverse encryption methods become crucial. This article offers an in-depth look at the various encryption methods, exploring their principles, applications, and significance in the digital era.
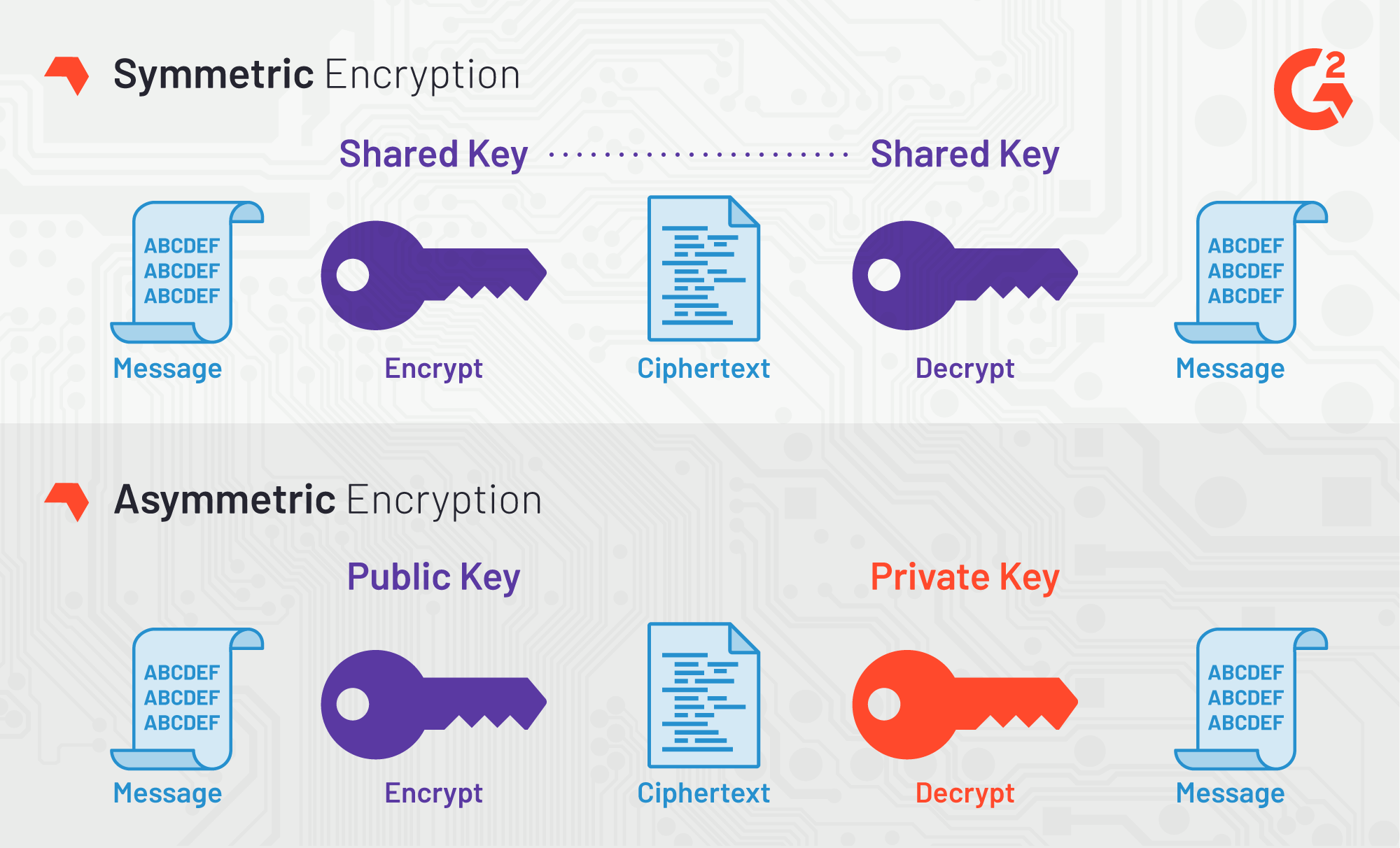
1. Symmetric Encryption: The Foundation of Data Security
Symmetric encryption, also known as secret key encryption, employs a single key for both encrypting and decrypting data. Its simplicity and speed make it ideal for securing large data volumes.
-
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
-
AES, with key sizes of 128, 192, and 256 bits, is a widely adopted global standard. It's the backbone of data security in countless applications, from encrypting files on a hard drive to securing sensitive government information.
-
2. Asymmetric Encryption: Enhancing Secure Communication
Asymmetric encryption, or public-key cryptography, involves two keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This method addresses the key distribution problem inherent in symmetric encryption.
-
RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
-
RSA, one of the earliest public-key systems, is fundamental in secure web browsing, email encryption, and digital signatures. Its security is based on the computational difficulty of factoring large integers.
-
3. Hash Functions: Ensuring Data Integrity
Hash functions convert data into a fixed-size hash value, ensuring data integrity and authenticity. They are crucial in digital signatures, data integrity verification, and password hashing.
-
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Series
-
The SHA series, including SHA-1, SHA-256, and SHA-3, are used in various security applications. They generate unique hash values that are virtually impossible to reverse-engineer.
-
4. Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC): Compact and Efficient
ECC offers the same security as RSA but with smaller key sizes, enhancing efficiency and speed, particularly in mobile and IoT devices.
-
ECC in Secure Transactions
-
ECC is used in digital currency platforms, secure email, and SSL/TLS for web browsing, providing robust security with reduced computational load.
-
5. Quantum Cryptography: The Future of Secure Communication
Quantum cryptography uses the principles of quantum mechanics to secure data. Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) is a notable application, offering a theoretically unbreakable encryption method.
-
BB84 Protocol
-
The BB84 protocol, developed by Bennett and Brassard in 1984, uses quantum mechanics to securely distribute cryptographic keys, immune to traditional eavesdropping techniques.
-
6. Homomorphic Encryption: Computation on Encrypted Data
Homomorphic encryption is a groundbreaking method that allows computation on encrypted data without decryption, offering unprecedented data privacy in cloud computing.
-
Applications in Cloud Computing and Data Analysis
-
This method enables secure data analysis and computation in cloud environments, allowing users to glean insights from encrypted data without exposing the raw information.
-
7. Steganography: The Art of Concealing Information
Steganography, the practice of hiding information within other non-secret data, is a unique approach to data protection, where the existence of the encrypted data is concealed.
-
Digital Watermarking and Covert Communication
-
Steganography is used in digital watermarking for copyright protection and in covert communications, where hiding the existence of a message is crucial.
-
8. Hybrid Encryption Systems: Combining the Best of Both Worlds
Hybrid encryption systems leverage the strengths of both symmetric and asymmetric encryption, often used in internet communication protocols for enhanced security and efficiency.
-
SSL/TLS Protocols
-
In SSL/TLS, a symmetric key is encrypted with a public key and sent alongside symmetrically encrypted data, combining the convenience of symmetric encryption with the security of asymmetric encryption.
-
Conclusion
Encryption is a multifaceted, evolving field crucial to data security in our digital world. From the widely used AES and RSA to the promising realms of quantum and homomorphic encryption, these methods collectively fortify the digital landscape against evolving cyber threats. As technology advances, so will encryption techniques, adapting to safeguard information and privacy in an increasingly interconnected global community.




Comments 0