
The Tor network stands as a complex and decentralized system designed to provide users with enhanced privacy and anonymity online. While widely recognized for its legitimate uses, such as safeguarding journalists, activists, and whistleblowers, Tor is equally infamous for hosting the Dark Web, a part of the internet where illicit activities thrive.
Why do people use Tor?
The Tor Browser, renowned for its capacity to provide anonymity, has become a refuge for a spectrum of users seeking to safeguard their online activities from prying eyes. Whether driven by a desire for privacy, a need to navigate restricted content, or even engage in illicit activities, individuals find varied reasons to adopt the Tor web browser.
Anonymity and Data Encryption
Tor excels in offering users a cloak of anonymity, shielding them from entities such as Internet service providers (ISPs), government agencies, advertisers, and cybercriminals. The robust data encryption provided by Tor is a magnet for those who seek to keep their online activities concealed.
Illegal trading
The dark underbelly of Tor manifests in its role as a black market for cybercriminals. It becomes a marketplace where hacking experts offer their services, and data brokers engage in the buying and selling of personal information, creating a haven for illegal trading.
Illegal materials
Tor's unique ability to host information inaccessible through conventional browsers makes it a repository for copyrighted material, government documents, and objectionable films and images, attracting users with a penchant for accessing content considered illegal by mainstream standards.
Whistleblowing
Tor serves as a shield for dissidents who dare to speak truth to power. Renowned figures like Edward Snowden have utilized Tor to expose illegal surveillance programs, emphasizing its pivotal role in safeguarding whistleblowers from potential reprisals.
Bypassing censorship
In regions where freedom of speech and expression is curtailed, Tor becomes a lifeline. By providing access to channels unavailable on the clear web, it enables individuals to communicate without fear of censorship or persecution.
Bypassing restricted content
The global variance in content availability prompts many users to turn to Tor for circumventing restrictions imposed by sites and streaming services based on geographical locations. Tor's capacity to unblock content and bypass geo-blocking facilitates unrestricted access.
Health privacy
In the realm of health issues, where privacy is paramount, Tor becomes a tool for concealing medical information from family members, insurance companies, and other prying entities, allowing users to maintain anonymity regarding sensitive health matters.
Journalism
Investigative journalism entities, recognizing the need for unhindered reporting, utilize Tor to conduct their work without fear of reprisal.
While Tor is often associated with activities outside the norm, it also finds users employing it for routine browsing with an added layer of anonymity.
How can I use Tor to browse the dark web?

The Tor Browser, designed for enhanced privacy and anonymity, goes beyond conventional web browsing by allowing access to .onion sites, a distinctive feature associated with the hidden corners of the internet, commonly referred to as the dark web. Accessing these sites is a straightforward process - users can input the .onion site's URL directly into the Tor Browser's address bar.
Contrary to the sensationalized narrative often linked with the dark web, which focuses on illicit activities like the trade of illegal goods and services, it is essential to recognize the broader context. While such activities do exist, the dark web serves purposes beyond these transactions.
It's crucial to understand that .onion sites aren't solely reserved for those seeking to operate in secrecy. In reality, they provide a means to bypass censorship, enabling users to navigate past country-level website restrictions. Major platforms, including Facebook, maintain .onion sites to offer users an additional layer of privacy. Similarly, established organizations such as the BBC utilize .onion addresses (e.g., https://www.bbcweb3hytmzhn5d532owbu6oqadra5z3ar726vq5kgwwn6aucdccrad.onion/), and the privacy-focused search engine DuckDuckGo can be accessed at https://duckduckgogg42xjoc72x3sjasowoarfbgcmvfimaftt6twagswzczad.onion/ (note that these .onion links are functional exclusively within the Tor Browser).
While locating .onion sites may not always be straightforward, several resources are available to assist users in their exploration. The Hidden Wiki or DeepWeb serves as a comprehensive directory of .onion sites, offering guidance for navigating the dark web. Additionally, the DuckDuckGo search engine indexes .onion sites, simplifying the process of discovering hidden content.
What can you find in Tor network?

The Tor network encompasses a diverse array of content, services, and activities. While the dark web is often associated with illicit or underground operations, it's important to note that not all content on the Tor network is illegal. Here's a breakdown of what you can find in the Tor network:
Legitimate and privacy-focused websites
Many individuals and organizations use the Tor network to host websites that prioritize privacy and security. This includes blogs, forums, and services that cater to users seeking enhanced anonymity and protection from surveillance.
Whistleblower platforms
Platforms like WikiLeaks have used the Tor network to provide a secure space for whistleblowers to submit sensitive information anonymously. This can include documents exposing government misconduct, corporate malfeasance, or other forms of wrongdoing.
Privacy-centric search engines
Specialized search engines like DuckDuckGo maintain a presence on the Tor network, allowing users to search the internet with a focus on privacy and avoiding tracking.
Online marketplaces
The dark web hosts various online marketplaces where users can buy and sell goods and services. While some marketplaces operate within legal bounds, others facilitate the exchange of illicit items such as drugs, firearms, or stolen data.
Forums and communities
The Tor network is home to numerous forums and communities covering a wide range of topics. These can include discussions on technology, privacy, politics, and more. However, some forums may also be dedicated to illegal activities or extremist ideologies.
Circumvention tools
Users in regions with strict internet censorship may find circumvention tools on the Tor network. These tools help individuals bypass restrictions and access information that might be blocked by their local authorities.
Educational resources
Researchers, academics, and enthusiasts contribute educational content on the Tor network. This includes resources related to privacy, security, and cryptography.
Illicit content and activities
The dark web does host illegal activities, including marketplaces for drugs, hacking tools, counterfeit currency, and more. There are also sites that share illegal content such as explicit material or copyrighted material without authorization.
It's essential to approach the Tor network with caution and adhere to ethical and legal standards. While it provides a platform for privacy-conscious individuals and legitimate activities, there are risks associated with engaging in illegal or harmful behavior on the dark web. Users should be aware of the potential consequences and use the Tor network responsibly.
Legal landscape of Tor
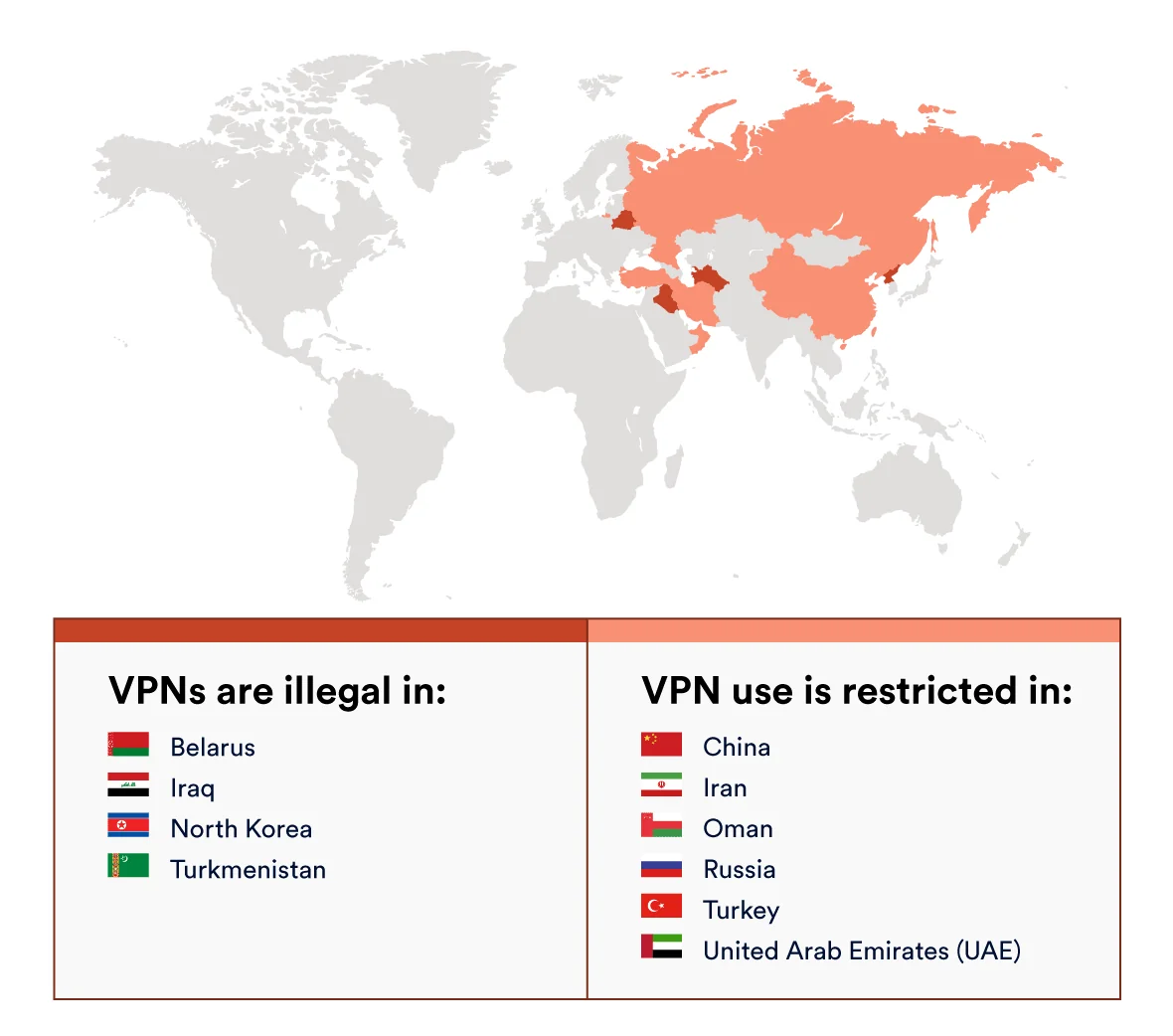
Tor shares a legal status akin to that of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) in many parts of the world.
In most countries, utilizing Tor technology itself doesn't typically pose legal issues. However, a caveat exists – engaging in illicit activities, such as procuring illegal items from deep web sites using Tor, may lead to legal consequences.
It's important to note that certain nations, like China, Belarus, and the UAE, not only prohibit VPNs but also express disapproval towards Tor. While downloading Tor won't necessarily lead to arrest, these countries may focus on blocking the technology rather than pursuing legal action against users. Nevertheless, exercising caution is advisable.
The legal standing of Tor is nuanced and varies across jurisdictions. Users are encouraged to be aware of the specific regulations in their respective countries to ensure compliance with local laws.
Drawbacks of Tor
While the encryption and multi-server routing of Tor contribute significantly to privacy protection, there are notable downsides to using this network. One prominent drawback is the considerable impact on internet speed, a factor that users should be prepared for when engaging in browsing activities through Tor.
The extent of the slowdown depends on various variables. A speed test conducted on a mobile device connected via Wi-Fi revealed a substantial difference. While the regular connection achieved downloads of 50Mbps, the same connection with Tor only managed 2Mbps. This considerable reduction in speed underscores the trade-off between enhanced privacy and compromised browsing efficiency.
Another potential issue arises from the fact that hackers frequently exploit Tor, utilizing it to shield their identities during cyber attacks. This has led many platforms to implement precautions. Some websites display warnings or even block access when they detect Tor usage. For example, PayPal subjected login attempts to additional security checks, blocking access in some cases. Amazon required users to approve notifications sent to their mobile devices before granting access. Google took a more stringent approach, blocking access to YouTube entirely due to the detection of 'unusual traffic from the computer network'.
Security of Tor
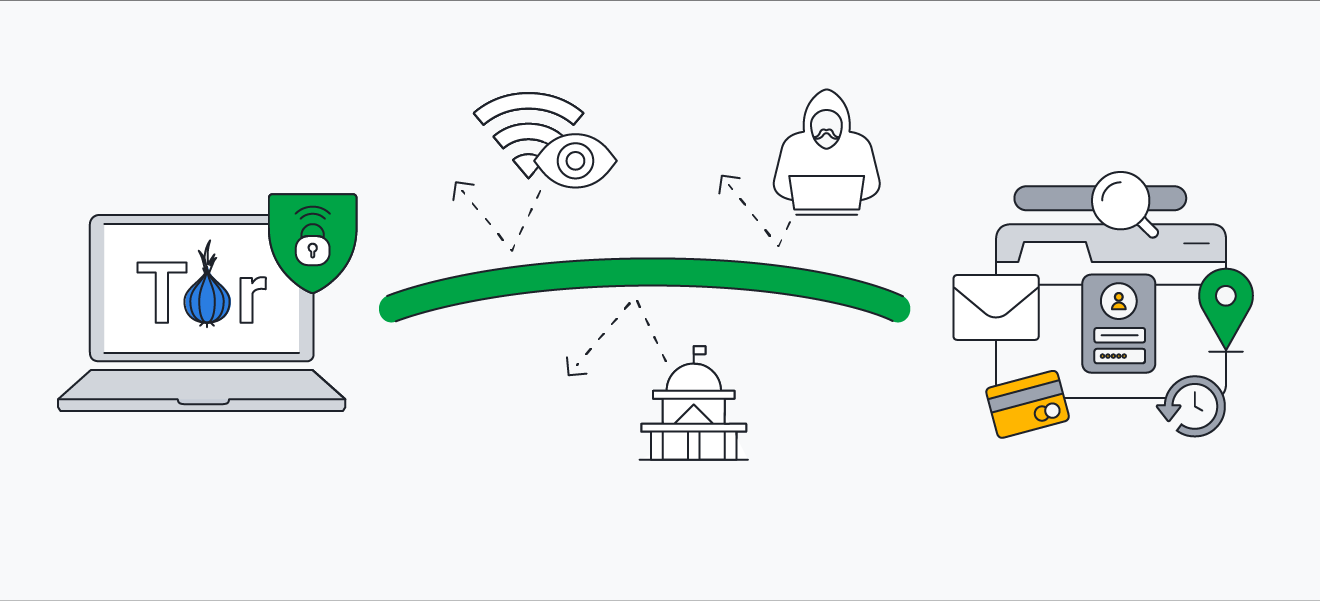
One of Tor's standout features in terms of security is its decentralized nature. Unlike networks controlled by a single entity, the Tor network operates through thousands of volunteers worldwide, each managing relays. This decentralized structure ensures that there is no singular point where someone can scrutinize connections or monitor data paths. For individuals seeking anonymity, this distributed approach offers a significant advantage.
However, it's essential to consider certain aspects that may impact Tor's security. While your internet service provider (ISP) won't be able to discern your online activities through Tor, it can identify that you are accessing the Tor network. In countries with limited support for web privacy, this might pose a concern for users.
Additionally, the first Tor relay, while not requiring logon credentials, possesses knowledge of your IP address. Although this information is limited, it's worth noting the potential exposure.
A potential vulnerability lies in the Tor exit node—the server responsible for removing the final layer of encryption and revealing the URL you're attempting to visit. If you're using an unencrypted HTTP connection instead of HTTPS, the exit node may be able to log sensitive information about your online activities, posing a potential risk.
Moreover, exit nodes can exploit a technique known as SSL stripping to access unencrypted HTTP communications on seemingly encrypted sites. Recent research by security expert Nusenu highlighted that up to 23% of Tor exit nodes were involved in a malicious campaign targeting accesses to cryptocurrency sites in 2020. This campaign involved altering traffic and redirecting transactions into the attackers' virtual wallets, underscoring the need for users to be mindful of potential risks associated with Tor exit nodes.
Combining Tor and VPN safely

While Tor is a formidable tool for preserving web privacy, it does come with certain considerations. For those seeking maximum protection, the most effective strategy involves combining Tor with a Virtual Private Network (VPN), though users should be mindful of the potential slowdown in service that accompanies this enhanced security.
One approach is to connect to a VPN first and then to Tor, a method known as 'Onion over VPN'. By doing so, your home network only registers your VPN IP, effectively concealing your access to Tor. The first Tor relay, in turn, solely sees your VPN IP address, ensuring that it remains oblivious to your identity. Simultaneously, your VPN is blind to the specific sites you're browsing, as that traffic is handled exclusively by Tor. This layered approach provides an added level of security, ensuring that even if a server is compromised, hackers cannot access your browsing history.
Conversely, 'Tor over VPN' does not shield users from potential threats posed by malicious exit nodes. Some users opt for an alternative method: connecting to Tor first and then to the VPN, a practice known as 'VPN over Onion'. However, this compromises privacy as the VPN gains visibility into your traffic.





Comments 0