
Tor (The Onion Router) has emerged as a technology for those seeking to preserve their anonymity online. Tor, originally developed in the mid-1990s by the United States Naval Research Laboratory, has since evolved into a non-profit organization's project aimed at facilitating anonymous communication across the globe.
What is Tor?
Tor, an acronym for The Onion Router, is an open-source software project designed to enable anonymous communication over the internet. Initially developed in the mid-1990s by the United States Naval Research Laboratory, Tor has evolved significantly, now operated by the Tor Project, a non-profit organization. Its primary aim is to enhance internet privacy and security by protecting users against traffic analysis, a form of network surveillance that threatens personal freedom and privacy, confidential business activities and relationships, and state security.
The foundational principle of Tor's operation involves directing internet traffic through a worldwide, volunteer-operated network consisting of more than seven thousand relays. This intricate process obscures a user's location and usage from anyone conducting network surveillance or analyzing traffic, making it extremely difficult to trace internet activities back to the user. By doing so, Tor enables its users to surf the web anonymously, protecting their personal identity and online activities from prying eyes.
Tor supports a variety of use cases, primarily aimed at individuals and organizations concerned about privacy and those under threat of censorship or surveillance. This includes journalists communicating with their sources, activists under repressive regimes, or businesses safeguarding sensitive information. Additionally, Tor allows users to access the "dark web", parts of the internet not indexed by standard search engines, where both legitimate and illicit activities coexist.
Is it legal to use the Tor Network?

Using the Tor network is legal in most countries around the world. The legality of Tor stems from its purpose as a tool for enhancing online privacy and security, allowing users to browse the internet anonymously. This anonymity is crucial for protecting freedom of expression, privacy rights, and enabling secure communication.
Tor is developed and distributed by the Tor Project. The software is openly available and free to use for various legitimate purposes, including protecting personal privacy, securing communication, and facilitating access to information, especially in countries with restrictive internet policies.
However, while the use of Tor itself is legal, it can be scrutinized in countries with strict internet surveillance laws or where internet usage is tightly controlled. In such cases, authorities may view the use of anonymity tools with suspicion, associating them with attempts to bypass censorship or conduct illegal activities online. Nonetheless, the mere use of Tor for privacy protection or accessing publicly available information remains legal and is often recommended for safeguarding one's digital identity.
It's important to note that the legality of actions performed over the Tor network depends on the nature of those activities. Like any tool, Tor can be misused for illegal purposes, such as accessing illegal content or engaging in unlawful transactions on the dark web. Such actions are illegal regardless of the technology used and can lead to legal consequences.
Which countries have banned the Tor Browser?
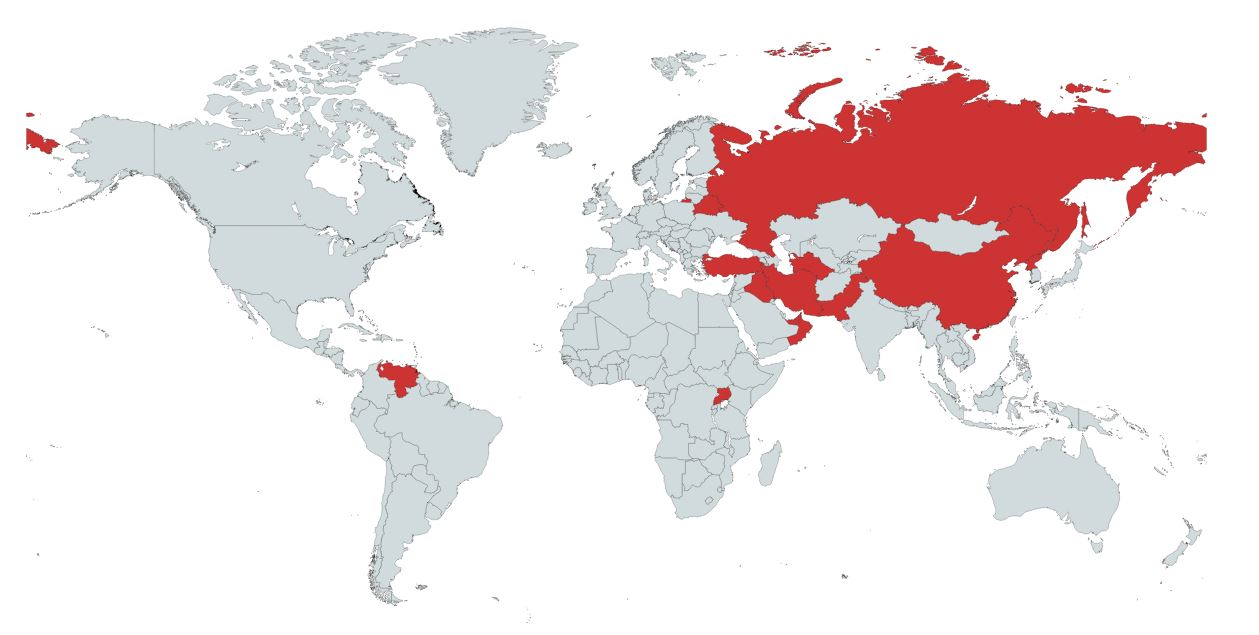
The Tor network has faced restrictions and outright bans in several countries around the world. These measures stem from various governmental concerns over privacy, security, and the potential for illicit activities. Here's an overview of countries where the Tor network has encountered significant barriers:
- China: Known for its rigorous internet censorship regime, China blocks the Tor network as part of its "Great Firewall", aiming to control and monitor internet usage within the country.
- Iran: In its effort to regulate internet access and maintain state security, Iran has implemented measures to restrict the use of Tor, especially to curb the flow of information during political unrest.
- Iraq: At times of heightened security concerns, Iraq has imposed bans on Tor to control communication channels.
- Russia: Aligning with its broader strategy to monitor and control the digital landscape, Russia has taken steps to ban the Tor network, limiting the ability for anonymous web browsing and communication.
- Belarus: Known for its restrictive internet laws, Belarus has taken measures to block the Tor network, aligning with its policies of internet regulation.
- North Korea: With one of the most restrictive internet access policies in the world, North Korea does not allow the general population access to the global internet, which includes a ban on the Tor network.
- Pakistan: Facing various internet regulations, Pakistan has at times blocked Tor, aiming to monitor and control the information that circulates within its borders.
- Turkey: In its attempt to curb dissent and manage the flow of information, Turkey has implemented restrictions on the Tor network, especially during times of political unrest.
- Venezuela: In the face of political turmoil and economic challenges, Venezuela has occasionally restricted access to Tor as a means to control online activities and information.
These actions against the Tor network highlight the tension between state desires for surveillance and control and the individual's right to privacy and free expression online. While these countries have implemented measures to restrict access to Tor, it's important to note that users often seek and find ways to circumvent such restrictions.
What are the legal uses of the Tor Network?
The Tor network supports a variety of legal uses that reflect its foundational goals of promoting freedom of expression and protecting individual privacy.
- Privacy protection: Individuals use Tor to protect their privacy from advertisers, internet service providers, and websites that track user behavior and personal information. Tor is instrumental in shielding users from invasive online tracking and surveillance.
- Secure communication: Journalists, whistleblowers, and activists often rely on Tor to communicate securely and share sensitive information without the risk of surveillance or reprisal. This use is particularly crucial in environments where freedom of speech is restricted and the press is censored.
- Research and education: Researchers and academics utilize Tor to conduct sensitive research, access academic resources anonymously, and circumvent censorship. This enables the free flow of information and ideas, essential for academic freedom and innovation.
- Circumventing censorship: In countries where the government restricts internet access and censors content, Tor provides a lifeline for citizens to access blocked websites, engage with the outside world, and exercise their right to information.
- Secure browsing: Tor is used for secure browsing by individuals who wish to avoid being targeted based on their internet activity. This includes avoiding targeted ads, evading surveillance, and accessing services without revealing one's location or identity.
- Protection for vulnerable populations: Victims of domestic violence, people living under oppressive regimes, and individuals in conflict zones use Tor to access critical information and services without revealing their whereabouts or activities.
These legal uses of Tor underscore its role in supporting internet users' rights to privacy, freedom of expression, and access to information. By facilitating anonymous communication and access, Tor serves as a critical tool for individuals and organizations worldwide to safeguard their digital rights and freedoms.
Conclusion
The legality of the Tor network is not a black-and-white issue; rather, it hinges on the balance between the right to privacy and the potential for misuse. Across the globe, Tor remains legal in most countries, championed for its role in protecting users' privacy, enabling secure communication, and offering a means to circumvent censorship. Its design and deployment reflect a commitment to upholding fundamental human rights, including freedom of expression and the right to privacy.
However, the legal landscape is nuanced and varies by jurisdiction. While Tor itself is a tool for anonymity and security, it is the users' responsibility to ensure their activities over the network do not infringe upon laws. The misuse of Tor for illicit activities is where legal issues arise, underscoring the importance of distinguishing between the technology itself and its application.





Comments 0